10 Challenges of Doing Business in Australia (With Solutions)


Explore the challenges of doing business in Australia and discover practical solutions, from navigating regulations to addressing operational costs.

- In this article
- Final Thoughts
Australia is an appealing destination for businesses, offering a stable economy, skilled workforce, and proximity to Asia’s booming markets.
Transparent regulations and competitive tax incentives make it seem like an easy place to start or grow a business.
However, beneath the surface of this business-friendly reputation, Australia has its own complexities that can trip up newcomers.
In this guide, we’ll break down the key challenges of doing business in Australia to help you navigate the process with clarity, even if you're unfamiliar with the local business environment.
1. Incorporation and Legal Registration
When talking about the challenges of doing business in Australia, let’s start with the basics first:
Challenge:
Registering with the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) is the first step to operating your business legally.
This process includes submitting ASIC Form 201, which assigns your business a unique Australian Company Number (ACN).
You’ll also need to register for an Australian Business Number (ABN) through the Australian Taxation Office (ATO).
After that, choosing the right business structure (sole trader, company, trust, or partnership) can be tricky, as each comes with unique tax, compliance, and liability implications.
Example:
For instance, if you are running an online business, you might think registering as a sole trader is easiest.
However, registering as a company would offer limited liability if you want to attract investors or protect personal assets.
Meanwhile, a partnership might work if you share responsibilities with others, though it involves joint liability.
Best Practices:
- Research structures: A company may suit growth-focused businesses, while sole traders or partnerships might work for smaller ventures.
- Start early with Director IDs: Obtaining a Director ID is now mandatory for all directors of Australian companies. The process can take longer for foreign-based directors due to the need for identity verification, so it's crucial to begin this step as soon as possible to avoid delays in incorporation.
- Consult an adviser: A local consultant can recommend the best structure based on your needs.
2. Construction Permits
After completing incorporation, the next step for many businesses is securing the necessary permits, especially if you plan to establish a physical presence.
Challenge:
If your business involves building a facility or modifying an existing property, you’ll need to navigate 11 procedures, including multiple inspections by local authorities.
These steps ensure compliance with building codes and safety standards but can delay projects if not managed properly.
Example:
For example, if you’re a cafe owner planning to add an outdoor seating area, you may need approval for structural changes and additional safety inspections. Potential delays in securing permits could push back the grand opening.
Best Practices:
- Engage local contractors: Professionals familiar with Australian regulations can help you avoid costly mistakes.
- Plan for contingencies: Allocate extra time and resources to manage unexpected delays.
- Document everything: Keep detailed records of applications, permits, and inspections to streamline communication with authorities.
3. Utility Connections
Once construction permits are in place, setting up utilities becomes the next critical task, requiring careful planning and coordination.
Challenge:
Getting utilities like electricity for a business property is more complex than for a residential setup. It involves completing forms such as the CT Metering Form and arranging internal wiring inspections.
Keep in mind that the entire process can take up to 75 days.
Example:
For instance, a small manufacturing unit requiring high-voltage electricity might face delays if the internal wiring doesn’t meet compliance standards. This could stall production schedules and lead to unforeseen costs.
Best Practices:
- Start early: Apply for utilities as soon as you secure your property.
- Coordinate inspections: Ensure your wiring and infrastructure meet standards to avoid rejections.
- Communicate with providers: Build a relationship with utility companies to expedite resolutions.
4. Funding Your Business
With utilities sorted, the focus often shifts to securing adequate funding – a step critical for business sustainability.
Challenge:
Securing funding is a critical step, and while Australia’s financial services sector offers various loans and venture capital options, eligibility criteria can be strict.
If your business falls into the innovation sector, you may qualify for government incentives like R&D tax offsets.
Example:
For example, if you have a tech startup developing AI software, you could benefit from an R&D tax offset.
This will provide up to 18.5% on eligible research expenditures.
However, it pays to check whether your business activities qualify, and you must document your activities thoroughly to prove your eligibility.
Best Practices:
- Prepare a strong pitch: Clearly outline your business plan, revenue projections, and funding needs.
- Explore grants: Look into sector-specific incentives, such as clean energy or technology grants.
- Compare lenders: Shop around for the best loan terms and conditions.
5. Tax Complexity
As your funding is secured, attention naturally turns to tax compliance, an area where many businesses face challenges.
Challenge:
Australia’s tax system includes multiple layers, such as federal and state taxes. Businesses face corporate income tax (30% or 25% for smaller businesses), Goods and Services Tax (GST), and payroll taxes.
So, it’s no wonder that understanding exemptions and transfer pricing rules for international operations can be overwhelming.
Example:
For instance, if you’re a retailer importing goods from overseas, you must comply with GST on the imported goods and ensure transfer pricing policies meet arm’s length standards.
Without proper documentation, you risk penalties during tax audits.

Best Practices:
- Use accounting software: Platforms like ANNA, Xero, or QuickBooks simplify tax tracking and reporting.
- Understand exemptions: For example, basic food items like bread may be GST-free, but cakes or pastries are not.
- Hire a tax expert: A professional can help you navigate compliance and optimise tax strategies.
Pro Tip From ANNA
Stay on top of your taxes effortlessly with ANNA's tools and expert support:
- Automatic tax calculations: Always stay informed about your tax obligations with real-time updates and optimised tax bills.
- Company income tax insights: Get a clear view of your upcoming tax bill based on expenses and income, making budget planning simple and predictable.
- Personalised tax calendar: Never miss a tax deadline with reminders tailored to your business needs.
- Expert accountant support: Have questions? Our friendly team of accountants is here to assist you.
- Annual Tax Return (BAS): From your first year of trading, ANNA manages your Business Activity Statement (BAS) to ensure seamless compliance.
- Goods and Services Tax (GST): Enjoy automatic GST calculations and direct reporting to the ATO for hassle-free tax management.
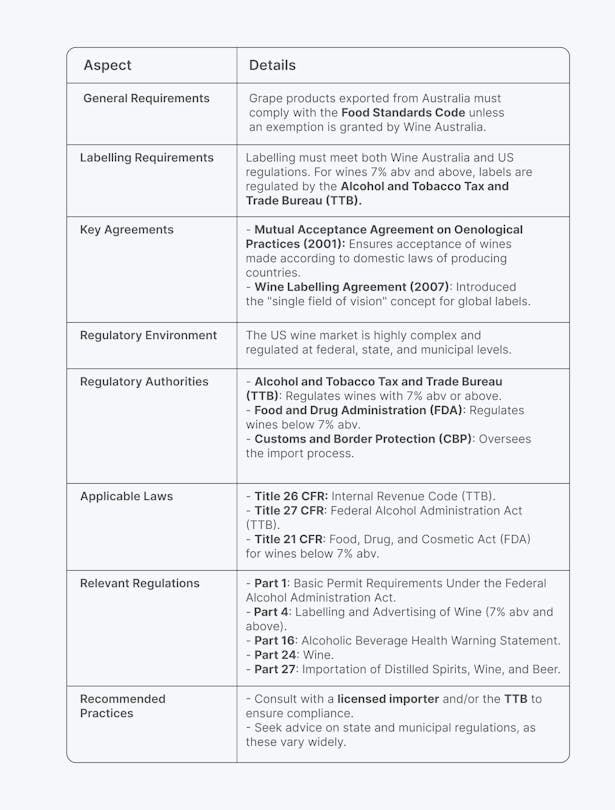
6. Import and Export Documentation
Proper documentation is crucial to ensure smooth cross-border trade, avoid shipment delays, and comply with customs regulations.
Challenge:
Trading across borders requires documentation for compliance with customs, product certifications, and import/export regulations. So, make sure that missing paperwork doesn’t delay shipments or result in penalties.
Example:
Take the example of an exporter of wine to the U.S. They must provide detailed records about the wine's origin, quality certifications, and proper labelling.
Ultimately, failing to meet these requirements could result in customs clearance issues.
Best Practices:
- Use customs brokers: These professionals can manage documentation and ensure compliance.
- Automate tracking: Invest in software to monitor shipments and avoid bottlenecks.
- Understand product-specific rules: Different goods have unique compliance standards.
7. Cultural and Market Dynamics
With operational processes like trade in place, understanding Australia’s cultural and market dynamics is key to building lasting business relationships.
Challenge:
Australia’s small but affluent market has unique consumer behaviours and preferences. So, understanding local dynamics is essential for successful market entry and long-term growth.
Example:
When Starbucks entered the Australian market, it encountered a unique coffee culture that favoured independent cafés over large chains.
This preference led to significant financial challenges for the company, resulting in losses of approximately $105 million within the first seven years.
Consequently, Starbucks closed around 70% of its underperforming locations, leaving only 23 stores nationwide.
The Starbucks experience in Australia shows the importance of humility, curiosity, and adaptability for global brands. Success in one market doesn’t always translate to another. Thus, thriving requires moving beyond assumptions and deeply understanding the preferences and values of local consumers.
Best Practices:
- Conduct market research: Tailor your offerings to meet local demand. For example, emphasise quality, sustainability, or local sourcing if these are important to your target customers.
- Build trust: Australians value straightforward and ethical business practices, so focus on transparency and integrity in your operations.
- Leverage partnerships: Collaborating with local businesses or influencers can help you build credibility and connect with the community.
8. Navigating the Legal System
While understanding market dynamics helps you establish a foothold, ensuring you navigate the legal system efficiently is equally important.
Challenge:
Australia’s legal system is efficient but requires familiarity with processes for resolving disputes, enforcing contracts, and managing insolvency issues. Not knowing the legal landscape can leave your business vulnerable.
Example:
A supplier dispute over late payments may escalate to legal action. For instance, if you haven’t outlined clear payment terms in contracts, you could face prolonged litigation and strained relationships with key partners.
Best Practices:
- Draft clear contracts: Ensure agreements outline obligations, timelines, and dispute resolution methods.
- Engage legal counsel: An experienced lawyer familiar with Australian laws can help you avoid pitfalls and manage legal complexities.
- Stay informed: Regularly review relevant regulations to understand your rights and obligations in different scenarios.
Pro Tip From ANNA
With ANNA One, creating professional invoices takes just seconds.
If a payment is delayed, ANNA follows up automatically, ensuring that 80% of invoices are paid within a week!
9. Data Protection and Privacy
Beyond legal compliance, safeguarding your business against data breaches is critical in Australia’s tightly regulated privacy environment.
Challenge:
Under the Notifiable Data Breaches (NDB) scheme, businesses must report breaches involving personal information that could cause harm. Non-compliance can result in heavy penalties and damage to your reputation.
Example:
For instance, a retailer experiencing a cyberattack where customer credit card details were exposed must report the breach to affected customers and the Office of the Australian Information Commissioner (OAIC). Failing to act swiftly could result in legal consequences and lost consumer trust.
Best Practices:
- Invest in cybersecurity: Use tools like firewalls, encryption, and regular audits to protect sensitive information.
- Train staff: Educate employees on identifying threats and following protocols to prevent breaches.
- Prepare a response plan: Have clear steps in place to identify, address, and report breaches quickly and effectively.
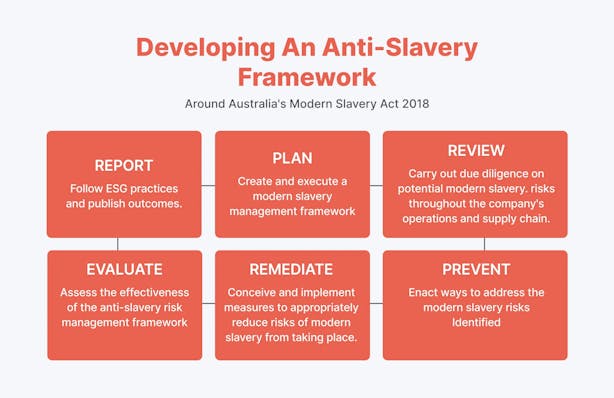
10. Environmental and Social Compliance
As data protection safeguards your operations, complying with environmental and social requirements is equally vital to align with Australian regulations and consumer expectations.
Challenge:
Australia’s Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) requirements are fragmented across federal and state jurisdictions.
Businesses with over A$100 million in annual revenue are also required to submit modern slavery statements, which detail their actions to mitigate slavery risks in operations and supply chains.
Example:
A large retailer earning over A$100 million annually must ensure its suppliers meet labour standards and document its due diligence efforts. Failure to comply could lead to fines and reputational damage, impacting both profitability and stakeholder trust.
Best Practices:
- Conduct supply chain audits: Regularly evaluate suppliers to ensure compliance with ESG standards.
- Monitor regulatory changes: Stay updated on new legislation, such as upcoming climate-related financial disclosures.
- Collaborate on sustainability: Work with suppliers and customers to promote shared goals, such as reducing carbon footprints or improving working conditions.
Final Thoughts
Starting or expanding a business in Australia offers exciting opportunities, but it also involves overcoming the unique challenges of doing business in Australia.
Taking advantage of best practices and learning from real-world examples can help you navigate these obstacles with confidence.
How ANNA Can Help New Businesses
ANNA equips your business with everything you need to start and operate smoothly, ensuring professionalism and compliance from day one.
Here’s how:
- Company Registration: ANNA simplifies the incorporation process by handling company registration (ACN) and ABN setup seamlessly.
- Virtual Office Address: Use a professional registered office address for official communications, helping to establish a credible business presence.
- Business Cards: Issue credit cards and virtual cards for your team, offering flexible payment options and easy expense tracking. Cards can also be integrated with Apple Pay and Google Pay.
- Tax Management: Stay compliant with automatic GST calculations, direct filing with the ATO, and a personalised tax calendar to track deadlines. ANNA also manages your BAS for the first year of trading.
- Bookkeeping and Invoicing: Automate financial tasks, including receipt matching, expense categorisation, and invoice generation, ensuring your records are always tidy and up to date.
- Comprehensive Support: ANNA’s friendly team of accountants and business experts is available to guide you through any questions or challenges.
Ready to start your business journey?
Sign up and let ANNA handle the details so you can focus on growing your dream business.






