How Much Is GST In Australia: Complete 2025 Tax Guide


Discover how much GST is in Australia, what it applies to, how it works, and what businesses and consumers need to know to stay compliant.

Confused about how GST works in Australia? This guide will clear things up.
We’ll explain what GST is, when it applies, how much you need to charge or pay, and what your obligations are. You’ll also get access to a practical tool that makes managing GST much simpler.
Let's get started!
What is the GST Rate in Australia?
As of 2025, Australia's Goods and Services Tax (GST) remains at a flat rate of 10%, a value that has been unchanged since its inception on July 1, 2000.
This tax applies to the majority of products and services sold or consumed in Australia, including imports, resulting in a broad-based consumption tax system.
The GST is a value-added tax, which means it is levied at every point of the supply chain but ultimately paid by the end user.
Businesses that register for GST can claim credits for the GST they pay on business-related purchases, essentially shifting the tax burden up the supply chain until it reaches the final consumer.
Though there have been debates about increasing the GST rate to solve budgetary issues, such measures have not garnered substantial political support due to fears about the possible impact on low-income households and the general cost of living.
Which Goods and Services Are Exempt?
GST does not apply to all goods and services in Australia.
Certain items are either GST-free or input-taxed, which means they are exempt from GST or have special tax status.
GST-free Goods and Services
These items are exempt from GST, although businesses can still claim credits for the GST they pay on inputs connected to these supplies.
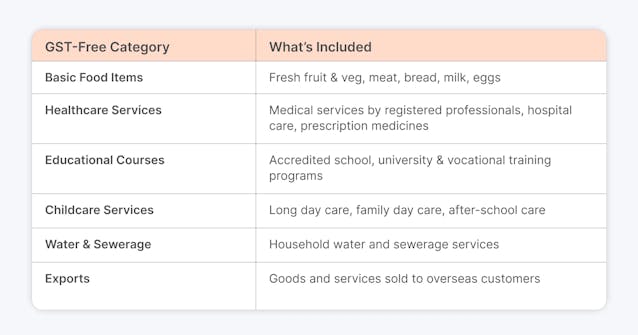
🔶 Basic Food Items - Unprocessed items, including fresh fruits and vegetables, meats, bread, milk, and eggs, are GST-free.
🔶 Healthcare Services - Registered practitioners' medical services, hospital treatments, and some health-related goods, such as prescription drugs, are all exempt.
🔶 Some Educational Courses - Accredited educational programs, including basic, intermediate, and postsecondary courses, as well as some vocational training, are exempt from GST.
🔶 Childcare Services - Approved childcare services, such as long day care, family day care, and after-school care, are exempt from GST.
🔶 Water and Sewerage - The supply of water and sewerage services is GST-free.
🔶 Exports - Goods and services exported from Australia are usually GST-free, which boosts international trade competitiveness.
Input Taxed Supplies
These supplies are not subject to GST upon sale. Therefore, businesses cannot claim credits for GST paid on associated inputs.
🔶 Financial Services - Financial services, including lending, borrowing, and securities transactions, are subject to input taxes.
🔶 Residential Rent - Renting out residential premises is input-taxed, which means landlords cannot charge GST on rent and cannot collect GST credits on associated expenses.
🔶 Existing Residential Property Sales - The sale of established residential properties is subject to input taxes, whereas new residential properties are subject to GST.
GST Registration Thresholds and Requirements
Understanding when and how to register for GST is critical for businesses looking to ensure compliance and optimise tax obligations.
How To Register for GST?
Follow these steps and apply for GST:
✅ Before you can register for GST, you must first obtain an ABN, which is an 11-digit business identifier.
✅ You can apply for an ABN when you register your business name or later on.
✅ Once you have an ABN, you can register for GST using any of the following methods:
✅ Online through the Australian Taxation Office (ATO). Online services for businesses
✅ Following registration, you will receive formal confirmation of your GST registration and effective date.
✅ Non-residents can use simplified GST registration if they sell to Australian customers and do not require an ABN or claim GST credits.
✅ The method is creating an AUSid account and registering online for an Australian Reference Number (ARN).
Mandatory GST Registration
If you have a business, you must register for GST if you achieve specific turnover thresholds:
🔶 Standard Threshold - If your business has a GST turnover (gross income excluding GST) of $75,000 or more in a given fiscal year, you must register for GST.
🔶 Non-profit Organisations - They have a higher threshold of $150,000.
🔶 Taxi and Ride-Sourcing Services - Regardless of turnover, you must register for GST.
Voluntary GST Registration
If your turnover is less than the mandatory threshold, you can choose to register for GST voluntarily. Voluntary registration enables you to:
🔶 Claim GST Credits - Reclaim the GST you paid on business purchases and expenses.
🔶 Increase Business Credibility - Being GST-registered can boost your credibility with suppliers and customers.
However, voluntary registration requires you to:
▶️ Charge GST on taxable sales.
▶️ Submit quarterly Business Activity Statements (BAS).
▶️ Maintain thorough records of sales and purchases.
GST Registration For Non-Residential Businesses
Non-resident businesses that supply goods or services to Australia may also need to register for GST.
The Australian Taxation Office (ATO) offers a simplified GST registration procedure to non-residents who:
▶️ Sell low-value products (A$1,000 or less) to Australian customers.
▶️ Offer digital products or services to Australian consumers.
▶️ Operate through electronic distribution platforms.
Under this system:
▶️ ABN - No ABN is required; instead, you will be issued an Australian Reference Number (ARN).
▶️ Simplified Reporting - Non-residents can lodge and pay GST quarterly using the ATO's online services.
▶️ Limitations - You cannot claim GST credits or generate tax invoices.
What is GST Return Filing Frequency
Businesses in Australia that have registered for Goods and Services Tax (GST) must file Business Activity Statements (BAS) in order to report and pay their GST obligations.
The frequency of these lodgments – monthly, quarterly, or annually – depends on the business's GST turnover and special conditions.
Monthly
It applies to businesses having a GST turnover of more than $20 million. By the 21st of the following month (for example, July BAS is due on August 21).
Reporting Details:
▶️ If the turnover is less than $10 million, you can use Simpler BAS (just report total sales, GST collected, and GST paid).
▶️ If turnover exceeds $10 million, complete reporting is needed, including more specific breakdowns (e.g., capital vs. non-capital purchases).
Quarterly
Quarterly reporting is the standard option for businesses with a turnover of $75,000 to $20 million.
BAS Due Dates:
- Q1 (July-September): 28 October
- Q2 (October-December): 28 February
- Q3 (January-March): 28 April
- Q4 (April-June): 28 July
Reporting Options:
▶️ Businesses under $10 million can use Simpler BAS.
▶️ Businesses exceeding $10 million use full reporting.
Annually
Annual reporting applies to businesses with a turnover of less than $75,000 that voluntarily register for GST.
When is it due?
▶️ If you file a tax return, it is due on the same date.
▶️ If not, the deadline is February 28, when the financial year ends.
▶️ You can pay quarterly and reconcile annually or pay in full once a year.
What is the Reverse Charge Mechanism?
In Australia, the reverse charge mechanism transfers responsibility for paying products and Services Tax (GST) from the provider to the recipient of certain products or services. This strategy is typically used for specialised imported services and business-to-business (B2B) transactions, particularly when the supplier is not located in Australia.
The reverse charge process applies under the following conditions:
🔶 Imported Services - When an Australian business buys services or digital products from a non-resident supplier and uses them in Australia.
🔶 B2B Transactions - In certain B2B transactions, the supplier is not registered for GST in Australia, but the recipient is or must be registered for GST.
Is There a GST Refund for Tourists in Australia?
Australia provides a GST refund to travellers through the Tourist Refund Scheme (TRS).
If you are visiting and intend to leave the country by air or sea, you can request a refund for the goods and Services Tax (GST) and Wine Equalisation Tax (WET) you paid on specific commodities.
To become eligible:
🔶 You must spend $300 (including GST) at the same store (same ABN).
🔶 The goods must be purchased within sixty days before your departure.
🔶 You must have a legitimate tax invoice that shows the store's information and the purchase amount.
🔶 The products must be taken with you as hand luggage (or displayed to an officer if checked in).
🔶 You must submit the products, invoice, passport, and boarding pass at the airport before departure.
🔶 Refunds are normally issued to your credit card, Australian bank account, or via cheque and are completed within 60 days.
Keep in mind:
✅ The system only covers physical things, not services, such as excursions, accommodation, or meals.
✅ You cannot claim for products you used in Australia or mailed home.
Key Points About GST
- GST Rate: The standard GST rate in Australia is 10%, unchanged since its introduction in 2000. This is a value-added tax paid by the end consumer, with businesses able to claim credits for GST paid on business-related purchases.
- Exemptions: Some goods and services are GST-free (e.g., basic food, healthcare, education, childcare, water/sewerage, exports) or input-taxed (e.g., financial services, residential rent, sales of existing residential property).
- Registration Thresholds: Businesses must register for GST if their turnover is $75,000 or more per year ($150,000 for non-profits). Taxi and ride-sourcing businesses must register regardless of turnover. Voluntary registration is also possible.
- Non-Resident Registration: Non-resident businesses can use a simplified GST registration process if they supply low-value goods or digital services to Australian consumers.
- Filing Frequency: BAS (Business Activity Statements) must be filed monthly (for turnover over $20 million), quarterly (for $75,000–$20 million), or annually (for voluntary registrants with turnover under $75,000).
- Reverse Charge Mechanism: Applies to certain imported services and B2B transactions where the supplier is not registered for GST in Australia.
- Tourist Refund Scheme: Tourists can claim a GST refund on eligible goods purchased within 60 days of departure, provided certain conditions are met.
- Sole Traders: Must register for and pay GST if their annual turnover is $75,000 or more.
- Invoicing: GST-registered businesses must include GST on invoices for taxable supplies.
- GST Calculation: To find the GST component in a price, divide the total by 11.
Conclusion
GST calculations are not exactly the simplest thing when you have a business. Although it is so, mistakes are not allowed, considering that you will then pay high fines. Fortunately, there is a tool that can automate this entire process for you: ANNA Money!
How Can ANNA Money Help You with GST?
ANNA Money is an all-in-one business tool that helps you handle everything from invoicing to taxation, with GST included.
It automatically calculates your GST and allows you to lodge with the ATO in just a few clicks, saving you time and eliminating the possibility of errors.
Besides that:
⭐ Business Documents - Keep receipts, invoices, and company records all in one location. We'll match transactions, extract important details, and make everything easy to find and share.
⭐ Business Account - Credit cards, virtual cards, Apple Pay, Google Pay, and employee expense cards. Easily check your balance and handle all of your payments.
⭐ Registered Office Service - Keep your personal address off the public record with same-day automated mail scanning and handling (compliant with ASIC, ATO, and other governmental authorities).
⭐ Matching Receipts - Automated receipt matching and spending categorization to ensure you obtain the proper tax relief
⭐ Personalised Tax Calendar - Never miss another tax date, and assure timely compliance with all of your tax requirements.
⭐ Support from Tax Experts - Our friendly support team will answer any query you have.
⭐ Bookkeeping Score - Stay on top of your bookkeeping and discover simple ideas for keeping your records neat.
⭐ Invoices - Professional-looking invoices in seconds - we can immediately chase any unpaid debts on your behalf.
⭐ Payroll - File payroll for yourself and your staff.
⭐ Annual Accounts and Company Tax Return - File your annual accounts with ASIC and your company tax return with the ATO straight through ANNA.
Sign up today and simplify your GST lodging!
FAQ
Do I Need To Pay GST As a Sole Trader?
As a sole trader in Australia, you must register for and pay GST if your annual turnover (gross business income before expenses) is $75,000 or more in any successive 12-month period.
Do I Need To Include GST on an Invoice?
If you are registered for GST in Australia, you must include GST on your invoice when you supply taxable goods or services.
How to Calculate GST Already Included in the Price?
Divide the total GST-inclusive price by 11 to find the GST component. The remaining amount after subtracting the GST is the price excluding GST.






