What does PAYG mean in Australia? [Definitive Guide]



- In this article
- What Is PAYG Withholding?
- Benefits of PAYG Withholding for Employees
- PAYG Withholding and the Role of Employers
- PAYG Instalments: A System for Business Owners and Investors
- How Are PAYG Instalments Calculated?
- What Happens If You Don’t Comply with PAYG Requirements?
- How Can ANNA Simplify Your Tax Management?
If you’re new to the workforce or running a business with employees, you’ve probably come across the term “income tax.”
It’s the money set aside from your earnings to meet tax obligations. But how does it work? How much do you need to pay?
That’s where the PAYG system steps in to simplify things.
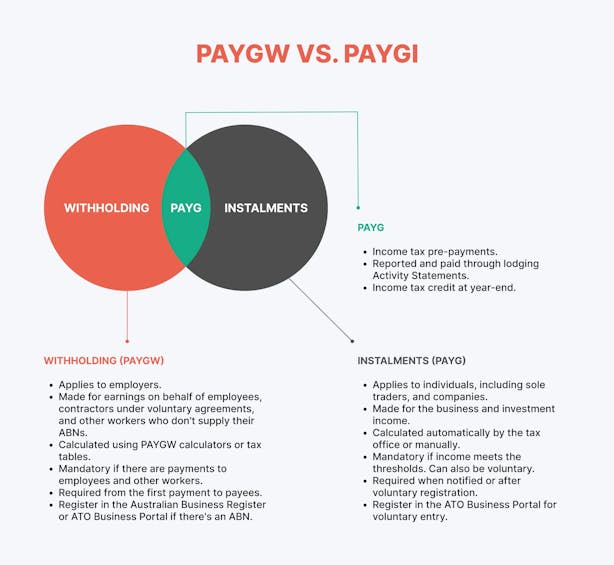
PAYG, or Pay As You Go, has two branches: PAYG Withholding (PAYGW) and PAYG Instalments (PAYGI).
While their names are similar, their purposes differ, and understanding them can make a big difference in staying on top of your taxes.
What Is PAYG Withholding?
PAYG Withholding is a system designed to help employees meet their income tax obligations in manageable portions throughout the year.
Under this system, employers are required to deduct a portion of an employee’s gross pay and send it directly to the ATO.
This deducted amount is referred to as PAYG Withholding.

The balance (your take-home pay) is what you receive in your bank account, either weekly, fortnightly, or monthly, depending on your employer’s pay cycle.
At the end of the financial year, the taxes withheld throughout the year are reflected in your income statement (previously called a group certificate or payment summary).
This helps you lodge your tax return and determine if you owe more tax or are eligible for a refund.
Why PAYG Withholding Matters for Employees
For employees, PAYG Withholding simplifies the process of meeting tax obligations. Instead of having to set aside money for tax on your own, your employer handles it for you.
This ensures that your tax liability is gradually paid off over the year, reducing the risk of being hit with a large, unexpected bill when you lodge your tax return.
Example 1: PAYG Withholding for an Employee
Let’s say Sarah works full-time as a graphic designer and earns $70,000 per year.
Her employer calculates the tax that needs to be withheld based on her income, which comes to approximately $13,000 for the year.
Instead of expecting Sarah to pay this amount in one lump sum, her employer deducts around $250 from her weekly pay and sends it to the ATO.
At the end of the financial year, Sarah’s income statement will reflect these withheld taxes, helping her file her tax return with confidence.
Benefits of PAYG Withholding for Employees
The primary benefit of PAYG Withholding is that it makes paying taxes manageable.
Rather than scrambling to save up for a large tax bill, employees contribute regularly, reducing financial stress.
However, employees still need to understand how the system works to ensure everything is in order.
❗ Key Considerations for Employees
- HELP/HECS Debt: If you’re repaying a student loan, such as a HELP or HECS debt, your employer may need to withhold additional tax.
- Second Jobs: If you take on a second job, you need to adjust your tax file number (TFN) declaration to avoid underpayment.
- Significant Changes: Changes in income, such as a promotion or a pay cut, may require adjustments to your PAYG Withholding.
Example 2: Adjusting PAYG for a Second Job
Tom is a teacher who recently started tutoring on weekends.
His main job withholds the correct tax for his $85,000 salary, but his tutoring income is taxed at a higher rate because it’s added to his total income.
Tom needs to ensure his PAYG Withholding from both jobs covers his total tax liability. If not, he might face a tax bill at the end of the year.
PAYG Withholding and the Role of Employers
For employers, PAYG withholding is a key responsibility. It involves not only managing their own tax obligations but also playing a vital role in assisting their employees to meet their tax responsibilities.
This involves deducting PAYG Withholding amounts from payments made to:
- Employees.
- Contractors who have entered into specific PAYG Withholding agreements.
- Businesses that fail to provide an Australian Business Number (ABN).
Registering for PAYG Withholding
Before making payments subject to withholding, employers must register for PAYG Withholding. This can be done online via the ATO’s Business Portal if the business has an ABN and myGovID.
For businesses without an ABN, registration can be completed by phone or using form NAT 3377.
Single Touch Payroll (STP)
Most employers now use Single Touch Payroll (STP) to manage PAYG Withholding.
STP is an automated system that allows businesses to report payroll information, including PAYG Withholding amounts, directly to the ATO.
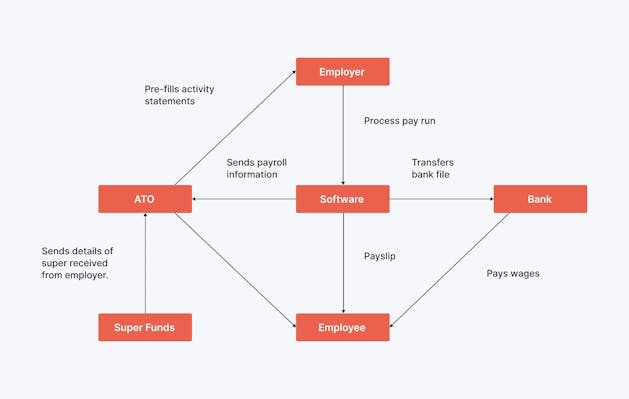
Employees can then access their income statements through their myGov accounts, eliminating the need for traditional payment summaries.
This system not only streamlines compliance for employers but also improves transparency for employees.
PAYG Instalments: A System for Business Owners and Investors
While PAYG Withholding is designed for employees, PAYG Instalments are aimed at businesses and individuals who earn income outside regular employment.
This includes income from investments, sole trading, or business activities.
PAYG Instalments allow you to prepay your income tax in regular intervals throughout the year. This is particularly helpful for avoiding a large tax bill when you lodge your tax return.
Example 4: PAYG Instalments for a Sole Trader
Emma runs a small bakery as a sole trader.
Her net income for the year is $120,000. Based on her previous tax return, the ATO estimates her tax liability to be $30,000.
Instead of waiting until tax time to pay the full amount, Emma makes quarterly PAYG Instalments of $7,500. This helps her manage her cash flow and avoids the stress of a large tax bill later.
How Are PAYG Instalments Calculated?
The ATO calculates PAYG Instalments based on your previous tax return or current income projections. You may have two options for calculating your instalments:
1. ATO-determined amount: Based on a fixed percentage of your income or a set instalment amount provided by the ATO.
2. Varying your instalments: If your income fluctuates or you anticipate a significant change, you can adjust your instalments.
However, it’s important to exercise caution when doing this. If your variation results in underpayment and your actual tax liability exceeds the instalments by more than 15%, the ATO may impose penalties or interest.
When Are PAYG Instalments Due?
PAYG Instalments are generally due quarterly, with payments required 28 days after the end of each quarter. The specific due dates are as follows:
- 1st Quarter: 28 October.
- 2nd Quarter: 28 February.
- 3rd Quarter: 28 April.
- 4th Quarter: 28 July.
These deadlines help spread out tax payments, making it easier to manage cash flow throughout the year.
How to Lodge and Pay PAYG Instalments
There are several ways to lodge and pay PAYG Instalments, including:
- Online through the ATO Business Portal or MyGov account.
- By mail, using payment slips provided by the ATO.
- Through a registered tax or BAS agent.
- Using electronic payment methods such as BPAY, credit cards, or debit cards.
Online payments are generally the most convenient option, as they allow you to meet your obligations quickly and securely.
Registering for PAYG Instalments
The ATO may automatically enrol you in the PAYG Instalments system if your income exceeds the entry threshold. Alternatively, you can manually register.
The thresholds for PAYG Instalments differ depending on your taxpayer type, such as individual, sole trader, company, or superannuation fund. For specific details, you should consult the ATO or your tax advisor.
Registration Methods
You can register for PAYG Instalments through the following methods:
- The ATO Business Portal or Online Services for businesses.
- Your registered tax or BAS agent.
- Standard Business Reporting (SBR)-compatible software.
- By calling the ATO business line as an authorised contact.
What Happens If You Don’t Comply with PAYG Requirements?
Non-compliance with PAYG requirements can result in serious consequences.
For employers, failing to withhold PAYG correctly may lead to penalties and the loss of tax deductions for payments made.
Businesses that underpay PAYG Instalments may face interest charges or penalties, particularly if the final tax bill is significantly higher than the instalments paid.
Special Considerations for Business Owners
Business owners, especially sole traders, have unique tax responsibilities. Unlike employees, their taxes are not automatically withheld.
This means they need to plan ahead and manage their cash flow carefully to ensure they can meet their tax obligations.
Consulting a tax professional can provide valuable guidance on how to manage PAYG Instalments and other tax requirements effectively.
How Can ANNA Simplify Your Tax Management?
ANNA provides a powerful, all-in-one solution for business owners, making tax management straightforward and stress-free.
From registration to financial organisation, ANNA streamlines the process to ensure you can focus on running your business without worrying about tax deadlines or filings.
📅 Comprehensive Tax Coverage
With ANNA, you can easily handle every aspect of your tax obligations, including:
- Company income tax
- GST management
- Annual tax filings
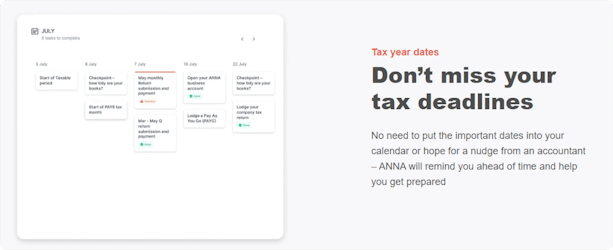
ANNA doesn’t just help you stay on top of deadlines – it simplifies every step of the tax process. By automatically calculating taxes and creating personalised tax calendars, it ensures you never miss a critical due date.
Additionally, you can optimise your tax savings with automatic expense sorting and file your taxes directly from the platform.
Key Features of ANNA for Tax Management
ANNA is packed with practical features that make managing your business taxes efficient and intuitive:
- Real-Time Tax Estimates: Stay informed about your financial obligations with accurate, up-to-date tax calculations. This gives you a clear picture of your liabilities at any moment.
- Expense Logging: Deductible cost is accounted for, helping you maximise your savings.
- Profit Tracking: Monitor your profits in real time to maintain a complete overview of your business’s financial health throughout the year.
- ATO Filing Support: Simplify tax submissions with ANNA’s integrated filing capabilities, ensuring your taxes are correctly lodged with the ATO during your first year of trading.
- Exportable Financial Records: Keep your records organised with exportable spreadsheets, making it easy to share financial data with your accountant or for personal reference.
How Does ANNA Work?
Managing taxes with ANNA is designed to be seamless and user-friendly. Here’s how it works:
- Connect Your Bank Accounts: Import all your business transactions into ANNA. The platform uses this data to accurately calculate your tax bill, ensuring every dollar is accounted for.
- Receive Real-Time Estimates: ANNA automatically tallies your sales and expenses, providing precise tax calculations. This transparency helps you plan ahead and avoid unexpected tax bills.
- Customise Your Records: You can manually add or adjust information at any time to ensure your financial data is complete and accurate, giving you full control over your records.
- File Your Taxes with Ease: ANNA’s clear and organised financial summaries make filing your tax return with the ATO straightforward and stress-free.
Ready to take the hassle out of tax management?
Sign up for ANNA One today and experience the professional efficiency that makes financial management simpler than ever.