
How to Start an LLC in Australia? - Everything To Know

Learn how to start an LLC in Australia and discover the steps, requirements, and tips to successfully establish your company.

Are you considering starting a business in Australia and wondering how to form a Limited Liability Company (LLC)?
This journey can be rewarding, providing flexibility and legal protection for your business.
However, understanding the complex requirements and processes of starting an LLC can be overwhelming for new entrepreneurs.
This article will help you navigate the process smoothly and ensure your LLC is set up correctly and legally, from choosing a business name to understanding your tax obligations.
Ready to get started?
Let’s first dive into the essentials of LLC in Australia!
What is an LLC in Australia?
An LLC (Limited Liability Company), also known as a Proprietary Limited Company (Pty Ltd), is a versatile business entity that blends features of both companies and partnerships.
It grants limited liability protection to its members (owners) while allowing flexibility in management and operations.
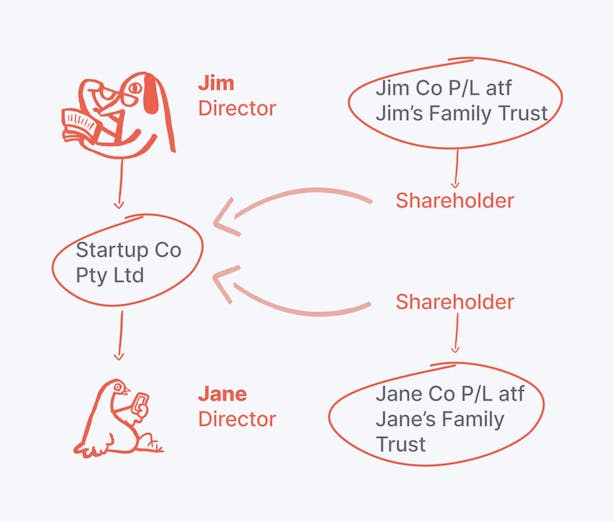
Unlike traditional companies, LLCs don’t issue shares to the public. Instead, they have members who hold ownership interests.
Types of LLCs in Australia
In Australia, when setting up a LLC company, you have 2 options:
1. Australian Limited Liability Company (Pty Ltd)
A private proprietary company is a separate legal entity from its owners.
It provides limited liability protection, meaning that shareholders are not personally liable for the company’s debts.
This structure is commonly used for small to medium-sized businesses.
2. Australian Public Limited Company (Ltd)
This structure is similar to a private proprietary company but allows for more shareholders and can raise capital from the public.
It’s commonly used for larger businesses that want to go public but remain unlisted on the stock exchange.
Essential Documents for Starting an LLC in Australia
Below is a summary of the documents required to register your LLC in Australia:
- Articles of Organization: Also called the Certificate of Incorporation, this legal document includes your LLC's name, registered office address, member details, and business purpose.
- Consent to Act as Registered Agent: If you appoint a registered agent, they must consent to take on this role.
- Identification Documents: Provide ID for members and the registered agent, such as passports or driver’s licenses.
- Operating Agreement: While not mandatory, an operating agreement is highly recommended. It details your LLC's internal operations and can prevent member disputes.
How to Start an LLC in Australia in 6 Steps?
Step 1: Choose a Business Name and Register Your LLC
Choosing a business name and registering your LLC is the first crucial step in starting a Limited Liability Company in Australia.
Your business name forms the foundation of your brand identity, making a lasting first impression on customers and setting you apart from competitors.
It should be:
- unique,
- memorable,
- easy to pronounce, and
- culturally sensitive.
Ensure your LLC name accurately reflects your business’s nature or services.
You can use the Business Name Check Tool provided by the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) to verify name availability.
Remember, availability doesn’t guarantee registration.
How to Register Your LLC Business Name?
Once you’ve chosen a unique name, register it with ASIC by following these steps:
1. Obtain an Australian Business Number (ABN): This is essential for all business operations and transactions.
2. Check Name Availability: Visit the ASIC website to check if your chosen name is available.
3. Register the Name: If the name is available, proceed with the registration on the ASIC website.
📌 Note
Registration doesn’t grant exclusive rights. Consider trademark registration for added protection.
Step 2: Create and Finalize Bylaws for Your LLC in Australia
After registering your LLC, the next step is to establish your company's governance. Here are your options:
Governance Options
- Replaceable Rules: Use the standard framework in the Corporations Act for managing internal affairs.
- Unique Constitution: Develop a custom constitution tailored to your LLC's needs for greater control.
- Hybrid Approach: Mix replaceable rules with your own provisions for a flexible and stable governance structure.
Considerations for Sole Director and Shareholder
An LLC with a sole director and shareholder doesn't need a formal governance system but should still document key operational procedures for clarity.
Drafting and Signing Bylaws
1. Draft the Bylaws: Outline rules and procedures for company operations, including decision-making processes, roles and responsibilities, and meeting procedures.
2. Review and Revise: Ensure the bylaws comply with the Corporations Act and reflect your LLC’s needs. Consult a legal professional if needed.
3. Sign the Bylaws: Finalize the bylaws and have all directors and shareholders sign them to formalize their commitment to the governance structure.
Whether using replaceable rules, a unique constitution, or a hybrid approach, well-defined bylaws ensure effective management and minimize conflicts.
Step 3: Appoint a Company Director and Other Statutory Officeholders
To form your LLC in Australia, you need a legal representative residing in Australia, known as the Company Director.
Every proprietary company must have at least one director who resides in Australia, responsible for:
- overseeing company affairs,
- ensuring compliance with the Corporations Act, and
- making key business decisions.
Foreign companies can appoint a Nominee Director, an external individual authorized to make legal decisions on the company's behalf.
Finding the Right Director
- Experience: Choose a provider with extensive experience in company incorporation, hiring staff, legal contracts, and liquidation.
- Reputation: Look for a provider with a proven track record in managing corporate affairs in Australia.
- Legal Expertise: Ensure the provider has a deep understanding of Australian commercial law.
Additional Statutory Officeholders
Depending on your LLC's size and structure, you may need to appoint other statutory officeholders, such as a company secretary or additional directors.
These roles help manage operations and ensure compliance with statutory requirements.
Remember, partnering with experienced professionals ensures your company meets all regulatory requirements and is well-positioned for success in the Australian market.
Step 4: Set Up a Business Bank Account
Setting up a business bank account for your LLC in Australia is crucial for effective financial management.
Follow these steps to ensure a smooth process:
#1. Understand the Legal Requirement
According to the Australian Tax Office (ATO), having a separate bank account is mandatory if your business is structured as LLC (Pty Ltd).
Additionally, you must maintain banking records for at least five years.
Many Australian businesses prefer online banking due to its simplified record-keeping.
#2. Choose the Right Bank
Research and compare business bank accounts from various institutions.
Traditional banks such as CommBank, NAB, ANZ, and Westpac offer robust business accounts.
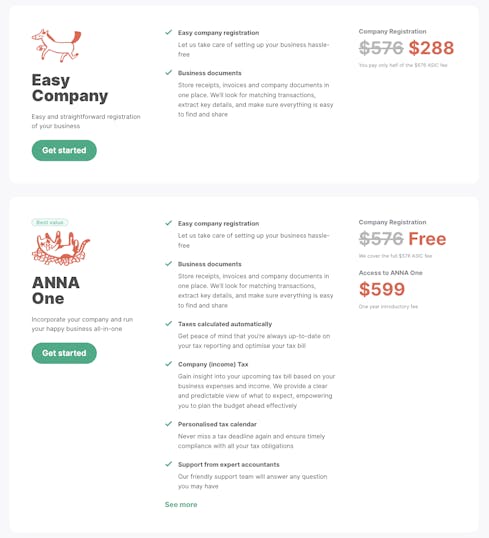
You might also consider newer players like ANNA, which provide:
- free company registration and
- a business account that manages bookkeeping, invoicing, GST, and company taxes.
#3. Gather Necessary Documents
Ensure your LLC is fully set up and registered for tax purposes. Collect the required LLC details and documentation for the account application, such as:
- Proof of LLC registration.
- Tax identification number.
- Identification documents of the directors and shareholders.
- Proof of business address.
#4. Select the Account Type
Business bank accounts may include transactional accounts and high-interest savings accounts. Look for features that match your needs, such as:
- Batch payments.
- Cloud-based accounting integration.
- Foreign transaction capabilities.
- Credit options.
#5. Open the Account
If you prefer a traditional bank, schedule an in-branch appointment to open your account.
For modern providers, you can complete the process online by submitting digital copies of the required documents.
Here’s how registration with ANNA looks like:
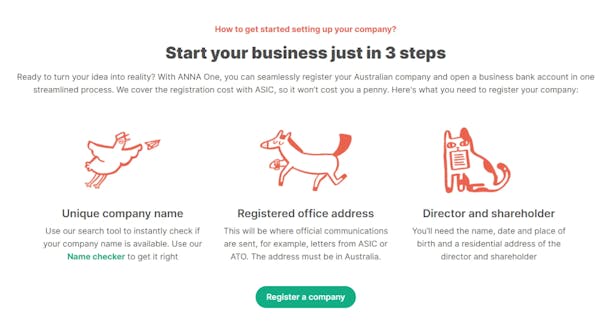
Step 5: Understand Tax Obligations
Understanding tax obligations is crucial when operating a Limited Liability Company (LLC) in Australia.
Here's a breakdown of the key tax requirements for 2024:
- Corporate Tax Rate: The standard corporate tax rate is 30%. However, eligible small businesses benefit from a reduced rate of 25%.
- Goods and Services Tax (GST): Companies with an annual turnover above AUD 75,000 must register for GST. This tax is collected on most goods and services sold or consumed in Australia.
- Pay As You Go (PAYG): LLCs must withhold amounts from employee payments and certain business transactions, then remit these amounts to the Australian Taxation Office (ATO). This system helps manage income tax obligations throughout the year.
- Fringe Benefits Tax (FBT): If your company provides non-cash benefits to employees, such as company cars or health insurance, it may be liable for FBT. This tax applies to the value of the benefits provided.
- State Taxes: Depending on your location, additional state or territory taxes may apply. These can include payroll tax, land tax, and stamp duty. Each state and territory has its own regulations and thresholds for these taxes.
It's essential to stay updated on tax laws as they can change and may include industry-specific taxes and incentives.
Consulting with a tax professional or accountant in Australia ensures you receive accurate and personalized advice.
Step 6: Verify Industry-Specific Compliance for Your LLC
Ensuring industry-specific compliance is essential for operating your LLC (Pty Ltd) in Australia.
Compliance requirements vary significantly depending on the sector in which your business operates.
This section provides an overview of crucial compliance areas and their importance in maintaining legal and operational standards.
Important Industry-Specific Compliance Requirements
1. Financial Services
- Compliance: Must comply with ASIC regulations.
- License: Obtain an Australian Financial Services License (AFSL) for providing financial advice or services.
2. Healthcare
- Registration: Requires registration with AHPRA.
- Standards: Adhere to health service standards.
3. Construction
- License: Must hold a building license from the relevant state or territory authority.
- Compliance: Follow the Building Code of Australia.
4. Food and Beverage
- Compliance: Adhere to FSANZ standards.
- License: May need a food business license from the local council.
5. Retail
- Compliance: Must adhere to consumer protection laws.
- Permits: May require specific permits for trading activities.
6. Manufacturing
- Compliance: Needs to comply with workplace health and safety regulations.
- Laws: Follow environmental protection laws.
7. Education and Training
- Registration: Must be registered with ASQA or TEQSA, depending on the education level provided.
8. Tourism and Hospitality
- Licenses: May require licenses for accommodation services, travel agencies, and tour operators.
9. Information Technology
- Compliance: Should comply with data protection and privacy laws, such as the Australian Privacy Principles (APPs).
It’s crucial to research and understand the specific compliance requirements for your industry, as non-compliance can result in penalties and legal issues.
For detailed information and guidance, it’s advisable to consult with legal professionals or industry associations in Australia.
And for other licenses and permits, utilize the Australian Business Licence and Information Service (ABLIS).
ABLIS provides information on licenses and permits at local, state, and federal levels, helping you find relevant approvals based on your business type and activities.
Key Points of LLC in Australia
Before we wrap things up, we would like also to introduce you to key points you need to know if you're thinking about starting an LLC in Australia:
1. Members
An LLC can have one or more members (owners). Members can be individuals, other companies, or trusts.
2. Management
LLCs can be managed by the members themselves (member-managed) or by appointed managers (manager-managed).
This flexibility allows for different management structures.
3. Taxation
LLCs are generally considered transparent for tax purposes. Profits and losses flow through to the members’ individual tax returns.
However, there are specific tax rules and regulations that apply to LLCs. Some of them are:
- LLCs are pass-through entities, not separately taxed like corporations.
- Profits and losses flow to individual owners (members), taxed as personal income.
- Benefit from international treaties that prevent double taxation.
- Liable for corporate taxes under local law but not required to complete audits.
4. Registration
To set up an LLC in Australia, you need to register it with the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC).
The registration process involves choosing a unique name, defining the company’s structure, and providing details about the members and their roles.
5. Legal Documents
LLCs typically have a constitution (internal rules) that outlines how the company will operate. They also have a shareholders’ agreement if there are multiple members.
The table below outlines other essential information for LLCs.
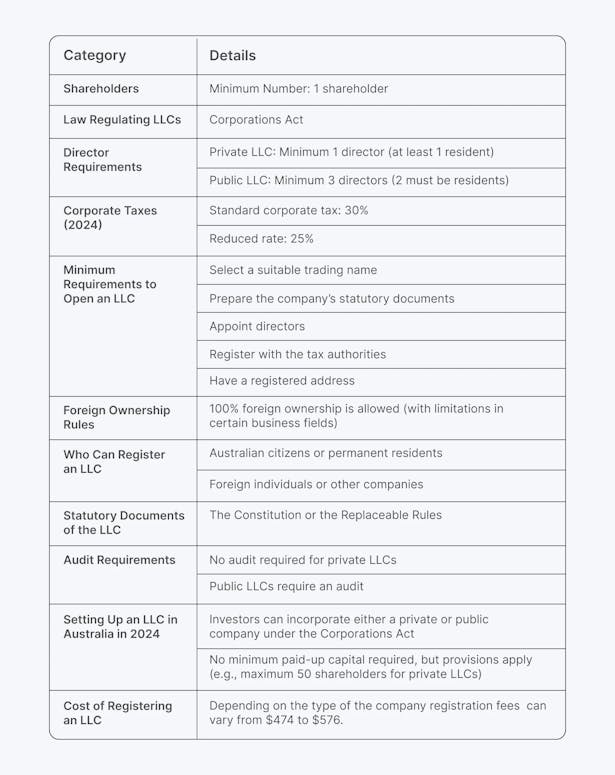
Pros & Cons

Conclusion
Starting an LLC in Australia is an exciting yet challenging journey.
With significant potential for success, it is crucial to navigate the complexities of registration, financial management, and compliance with careful planning and the right support.
This is where ANNA can help you.
With its ANNA One package, you can seamlessly register your Australian company and open a business bank account in one streamlined process.
Key Benefits of ANNA One:
- Stay on top of company income tax, GST, and annual filings without the stress.
- Ensure your expenses are categorized correctly for maximum tax efficiency.
- Keep your financial records tidy and organized, boosting your business’s credibility and operational efficiency.
- Never miss a crucial deadline with ANNA’s proactive notifications.
Getting started is simple:
1. Select a Company Name: Use ANNA’s platform to ensure your chosen name is available and complies with ASIC guidelines.
2. Enter Your Business Details: Provide the necessary information about your business.
3. Relax While ANNA Registers Your Company: ANNA handles the entire process with ASIC, from start to finish.
Ready to turn your business dream into reality with ease and efficiency?






